ERP
ERP may refer to any of the following:
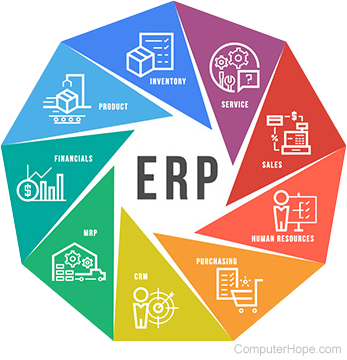
1. Short for enterprise resource planning, ERP is a business system that integrates multiple applications relating to accounting, human resources, inventory, orders, shipping, and services. ERP systems are widely used since the early 1990s and fall under the umbrella of enterprise applications, as larger businesses often use them. However, there are less complicated, small business versions of ERP software as well.
Types of ERP systems
Today, many ERP systems (ERP suites) run in the cloud as a SaaS (Software as a Service). A cloud ERP makes it easier and more secure for businesses to manage their information. These systems can be maintained by a company specializing in the upkeep of servers and databases, and security. This service makes it easier to scale as your business grows.
For companies that cannot have or do not want their data in the cloud, on-premise ERP can run on a company's data center. Alternatively, a company can have a hybrid ERP that runs some of their systems in the cloud and other systems on premise.
Examples of ERP systems
Below are a few examples of ERP systems that can be implemented in a business.
Why would you need ERP?
For a business or enterprise, having ERP helps bring all your business information and tasks into a central location. For example, a business may handle their accounting in a program like QuickBooks, customer data in a CRM (customer relationship management), orders in a custom program, and create reports in Excel. Each of these products are silos of information that don't communicate with each other. Requiring your employees to use each of these systems separately makes them inefficient, increases operational costs, introduces problems, and makes it difficult to find business insights. An ERP brings separate entities into one system, providing an efficiency increase for employees and the business, and helps lower overall running costs.
What is the difference between a CRM and ERP?
A CRM often only deals with the interaction between your company and its customers. A CRM helps automate, streamline, and track those interactions with your customers. However, an ERP goes beyond only handling the customer tasks and can incorporate your employees, money, manufacturing, distribution, and your CRM systems into a central, single system. Small businesses may only need a CRM system, as they're more affordable and don't have enough systems that need to communicate with each other. However, larger companies and enterprises need ERP to stay competitive and operate efficiently.
How do ERP systems work?
An ERP system is designed using a collection of ERP modules (ERP applications) that are each designed to meet a specific part of a company's needs. Each of the ERP modules communicate with each other by sharing a central database. For example, a company may start with an ERP system with human resources, inventory, finance, and sales modules to help run their company. As the company grows and has new or increased needs, these modules could be customized further with additional modules.
What are the advantages of ERP systems?
A properly designed and integrated ERP system that stores and shares all company information has the following advantages.
- Help automate and streamline many processes, increasing the overall productivity of your company and employees.
- Helps manage finances and taxes, and saves money for the company.
- Easier to manage all aspects of your supply chain.
- Improves collaboration between all departments and employees.
- Allows your company to stay more compliant.
- Improved analytics that can give you better business intelligence on all aspects of the company in one location.
- Allows for better reporting capabilities.
What are the disadvantages of ERP systems?
Some argue that ERP is an absolute requirement for an enterprise. However, there are still disadvantages of implementing ERP.
- Have a high cost to implement.
- Can be difficult to implement and transition to from existing systems.
- Requires retraining all employees.
- ERP modules may be too generic for some companies and require additional modules or custom modules for specific business needs.
2. With gaming and chat, ERP is short for erotic role play and describes any role-playing that focuses on physical intimacy.
Business terms, Computer abbreviations, CRM, EDI, Game terms, Module, MRP, SAP
