File system
Alternatively known as file management or FS (File System) is a method of organizing and retrieving files from a storage medium (e.g., hard drive). File systems usually consist of files separated into groups called directories. Directories can contain files or additional directories. Today, the most commonly used file system with Windows is NTFS (NTFS File System).
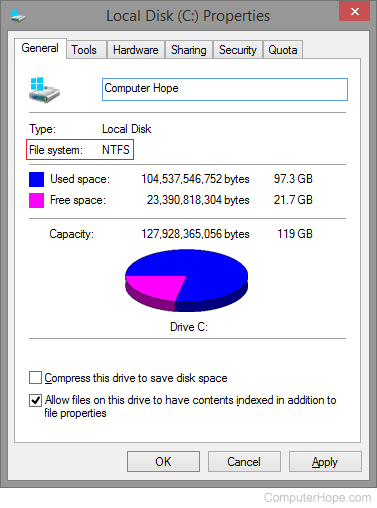
Without file management, all files would have no organization, and it would be impossible for a file with the same name to exist. Files are often managed in a hierarchy, which lets you view files in the current directory and then navigate into any subdirectories.
Examples of file systems
Over the evolution of computers, there have been different file systems used. Below are links to the most common file systems.
- exFAT
- FAT (File Allocation Table) (e.g., FAT16 and FAT32)
- GFS (Global File System or Google File System)
- HFS (Hierarchical File System)
- HPFS (High-Performance File System)
- NTFS (NTFS File System)
- UDF (Universal Disk Format)
How are files managed by the user?
To manage and organize the directories and files on their computer, they use a file manager. For example, in Microsoft Windows, you'd use Explorer, a file manager.
Which file systems did Microsoft Windows 95 not support?
1. NTFS
2. ext3
3. HPFS
4. All of the above
Computer acronyms, Directory, Drive management, File, Fstype, HPFS, Journaling file system, Operating system terms, Partition, System component
