Window
A window may refer to any of the following:
1. A rectangular section of the computer's display in a GUI (Graphical User Interface) that shows the program currently being used. For example, the browser window you're using to view this web page is a window. Windows allows users to work with multiple programs or view multiple programs at once. Almost all windows allow you to minimize and maximize them, allowing you to hide and view a program temporarily. Below is what a window may look like in Microsoft Windows, and each of its major features called window elements.
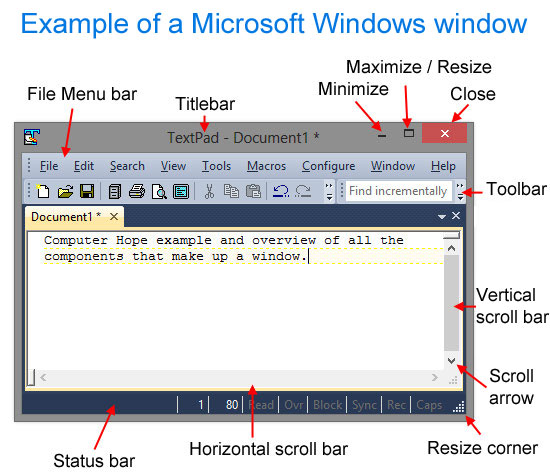
If a window is not fullscreen (maximized), it's in window mode. In this mode, the window can be moved around the screen by clicking the title bar and dragging it around the screen.
Links to window elements
Below are links to each window elements shown in the picture above. Clicking any of these links gives you further information about that window section.
- Control menu
- File menu bar
- Title bar
- Minimize
- Maximize / Resize
- Close
- Toolbar
- Vertical scroll bar
- Resize corner
- Horizontal scroll bar
- Status bar
How is a window opened?
A window is opened when a program or file is opened by clicking or double-clicking an icon. For example, when you open Notepad, the Notepad window is shown. If you open a text file, that file opens in Notepad by default but can also be opened in any other text editor.
In Microsoft Windows, you can have multiple windows open at once and switch between open programs by clicking the program icon in the taskbar or using the shortcut key Alt+Tab.
2. Window is the name of a transition.
Active window, Cascade, Close, File menu bar, Fullscreen, GUI, Horizontal scrolling, Inactive window, Maximize, MDI, Minimize, Modal window, Motif, Operating system terms, Restore, Restore down, Scroll bar, Sizing handle, Status bar, Tiling, Title bar, Toolbar, UI, Windoid, Windowed mode
