DApps

Short for decentralized apps or decentralized applications, DApps are software applications that run on a decentralized network, usually a blockchain or other DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology). Unlike traditional applications, which are hosted on servers and controlled by a single entity, DApps are designed to operate in a distributed manner.
While similar in functionality and utility to typical apps, DApps differ in that they operate autonomously (without human intervention), usually by utilizing smart contracts. DApps distribute tokens to users through an algorithm. As a result, full control and ownership are kept from belonging to a specific individual or company.
DApps can cover multiple use cases, from DeFi (Decentralized FInance) platforms and decentralized social networks to gaming, supply chain management, and others. Probably the most well-known example of a decentralized application is bitcoin.
DApps structuring
The following diagram shows how DApps are structured relative to ISPs (Internet Service Providers) and other connected devices.
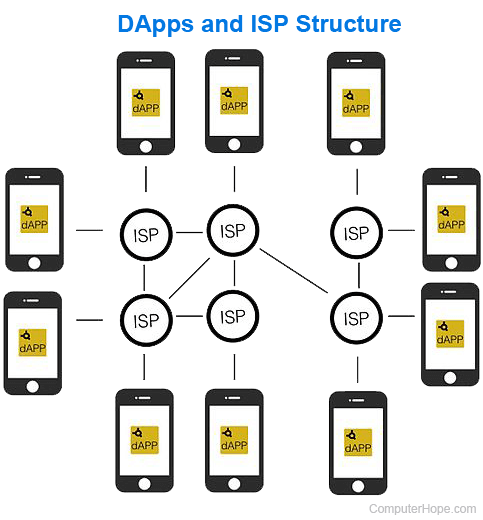
Blockchain, Computer acronyms, Cryptocurrency, Crypto terms, Decentralization, Entity, Ethereum, Network terms, Server, Smart contract, Software terms, Token, Web3
