ALU
Short for Arithmetic Logic Unit, the ALU is a complex digital circuit with an AU (Arithmetic Unit) and a LU (Logic Unit). There are multiple Arithmetic Logic Units in a computer, including multiple ALUs in the CPU (Central Processing Unit), GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), and FPU (Floating-Point Unit).
The computer Central Processing Unit ALU performs bitwise and mathematical operations on binary numbers and is the last component to perform calculations in the processor.
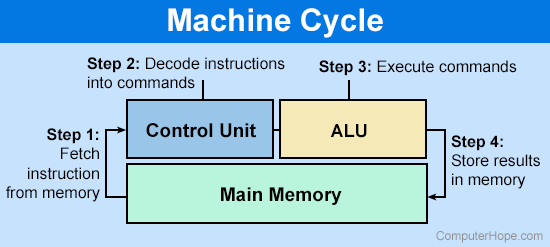
The ALU uses operands and code that tells it which operations to perform for input data. After the ALU processes the information, it's sent to the computer's memory.
The first and maybe the most famous ALU was the 4-bit Intel 74181 released in 1970. It was the first ALU placed in a single chip.
Arithmetic operations
The arithmetic unit handles all of the following computer numerical operations.
- Add - add two bits.
- Add with carry - add two bits with a carry-in.
- Subtract - subtract two bits.
- Subtract with borrow - subtract two bits with borrow from carry-in.
- Negate - flip the bits values sign (- to + or + to -).
- Increment - add 1 to a bit.
- Decrement - subtract 1 from a bit.
- Pass through - let bits through without modification.
Simple ALUs have no divide or multiply operations. These ALUs perform these operations using the add and subtraction operations.
Logic unit operations
The logic unit performs logical operations (e.g., AND, OR, and NOT) and numeric tests like checking if a number is a negative number.
Accumulator, Architecture, Arithmetic, Boolean, Computer acronyms, Control Unit, CPU terms, Logic gate, Machine cycle, Main memory, TLA, Von Neumann Architecture
